Supply and Demand
Now we will delve into the topic of supply and demand. What is demand and how does it operate?
Demand is the behavior of the buyer and how the buyer makes purchasing decisions. Demand is all about what we, as buyers, desire.
If we had unlimited resources, we could purchase everything we ever wanted at any price. However, in reality, each person has limited resources, and we have to choose between purchasing one item over another.
The primary factor in these decisions is price. All things being equal, the cheaper something is, the more customers will want to buy it. Conversely, the more expensive something is, the fewer customers will want to buy it. The law of demand revolves around price.
The law of demand can be defined as follows: as price increases, quantity demanded decreases; as price decreases, quantity demanded increases.
There is an inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded.
Study Tip: Under the law of demand, as price increases, quantity demanded decreases. There is an inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded.
Let’s illustrate the law of demand with a graph.
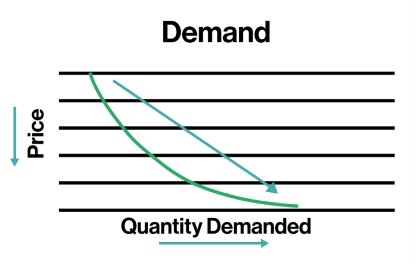
We have price along the Y-axis and quantity demanded along the X-axis. Then we have the demand curve. It’s crucial to distinguish between changes in quantity demanded and changes in demand. A change in quantity demanded represents a change along the demand curve, while a change in demand indicates a shift in the actual demand curve.
The demand curve slopes downward because as price decreases, quantity demanded increases. Buyers want to purchase more of something when it’s cheaper. You can think of the “D” in demand as signifying “down” for the law of demand.